
Beyond the Hit: Understanding Concussions
- carolinecannon20080
- Jan 28
- 5 min read
Beyond the Hit: Understanding Concussions
Concussions are a type of traumatic brain injury that occurs when the brain is jolted or shaken inside the skull. Concussions can have serious and long-lasting effects on cognitive functions, physical coordination, and emotional health. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and long-term risks of concussions is crucial for both prevention and effective treatment. Read the following blog to learn more about the truth and dangers of concussions.
What is a Concussion?
A concussion is a type of brain injury that happens when the brain is moved around inside the skull. It can temporarily disrupt normal brain activity, leading to a range of symptoms such as headache, dizziness, confusion, nausea, and sensitivity to light or sound. In some cases, individuals may experience memory problems, difficulty concentrating, or changes in mood. While most concussions are mild and the symptoms resolve over time, the effects can vary in severity, and repeated concussions may lead to long-term health issues. Proper care and rest are essential for recovery to avoid further complications. Roughly 4 million concussions occur nationwide every year, making it the most common head injury.
What Causes Concussions?
When the head is hit, the sudden movement can stretch and damage brain tissue. The damage to the brain can trigger a chain of harmful changes within the brain that interfere with normal brain activities. There are many ways concussions can occur, however the most common ways to get concussions are with sports and car accidents. A study done with UPMC shows that between 1.7 and 3 million sports- and recreation-related concussions happen each year. Around 300,000 of those are from football. Another common way to get concussions are by falling, which is dangerous but especially for elderly. Here are the most common causes of concussions:
· Sports injuries- Contact sports like football, hockey, soccer, and boxing are common sports with concussion injuries. Athletes can experience blows to the head or collisions with other players or the ground, causing the brain to be jolted around.
· Falling- Falls, especially in older adults or young children, can lead to a concussion if the head hits a hard surface, such as the ground, floor, or furniture.
· Vehicle accidents- Car accidents, especially those involving sudden stops or collisions, can cause a person’s head to jerk violently, leading to brain injury. Falls while cycling or skateboarding without protective gear (like helmets) can easily result in concussions.
· Physical fights- Blows to the head during fights or domestic violence incidents can cause concussions.
Types of Concussions and Severity
The severity of the concussion can determine how the brain responds to the damage. There are 6 main kinds of concussions, cognitive fatigue, vestibular, ocular, post-traumatic migraine, cervical, and mood.
· Cognitive Fatigue- This type of concussion causes someone to have trouble with mental tasks. This can limit the ability to multi-task, feel less focused, and have trouble retaining information.
· Vestibular- This type of concussion can cause people to feel off balance. This causes people to have trouble coordinating.
· Ocular- This kind of concussion causes people to have trouble with visual tasks like reading long passages and moving eyes together
· Post-Traumatic Migraine- This concussion impacts all the senses. This causes people to feel overwhelmed by loud places. This tends to lead to headaches, nausea, and sensitivity to light/noise.
· Cervical- This type of concussion causes trouble with stress or pressure on the neck, spine, or spinal cord. Slouching and holding heavy things can make the symptoms worse.
· Mood- This type of concussion makes it hard to turn off your thoughts. You might have excessive worry and feel restless. This can make social interactions difficult as well as limiting normal activities.
All concussions are dangerous to the brain, however the more concussions that occur, the more dangerous the results can be. A study done with the University of Oxford shows that those who had four or more mild concussion episodes also showed worsened processing speed and working memory. Each additional reported concussion was linked to progressively worse cognitive function. The repetition of severe concussions can lead to Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE). The symptoms of CTE can include memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, impulse control problems, aggression, depression, anxiety, suicidality, parkinsonism, and progressive dementia.
Symptoms of Concussions
The symptoms from concussions can range but can also impact different parts of the body including the physical body, cognitive functions, as well as emotions.
· Headache- the movement/tension on the brain as well as the autonomic nervous system tensing up muscles in the head an neck can cause severe headaches after a concussion occurs
· Vomiting- Throwing up usually occurs due to increased intracranial pressure or disruption of brainstem function, which can affect the body's vomiting center. Additionally, concussions can impact the vestibular system and autonomic nervous system, leading to nausea and vomiting.
· Confusion- being confused after a concussion is caused from the disruption of normal brain function, particularly in areas responsible for processing information and maintaining cognitive clarity.
· Vision Changes- Vision changes after a concussion occur because the injury can affect the brain areas responsible for processing visual information, leading to symptoms like blurred or double vision. Additionally, disruptions to the vestibular system or eye coordination can cause difficulty focusing or maintaining proper eye alignment.
During and after the concussion, there is typically a painful headache, confusion, and being extra sensitive to light and noises.
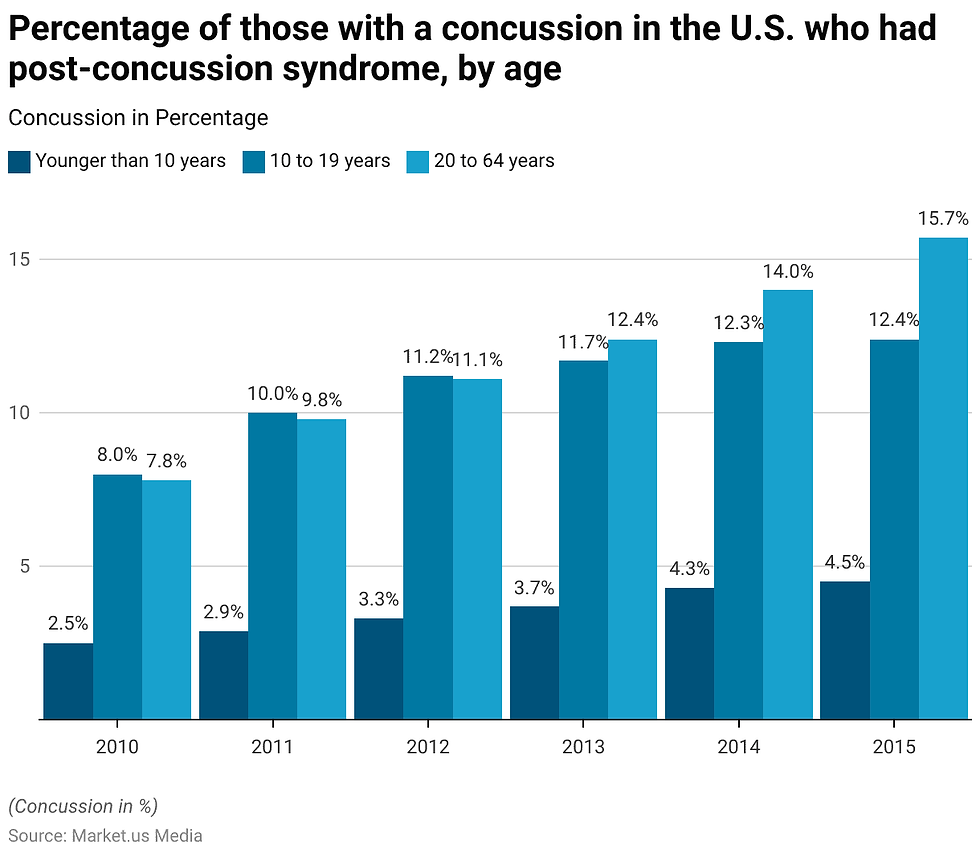
Concussion Prevention
There are many ways to prevent concussions from occurring and impacting your everyday life. For elderly and young children, preventing falls can be done by installing handrails on the stairs or in the shower. For motor accidents, wearing a seatbelt can help keep the body and head in place more effectively in a car accident than not wearing one. During physical sports, wear appropriate head protection and be cautious with the placement and use of the head. While riding a bike or skateboarding, wear a helmet and appropriate headgear.
The brain is the control center of our entire body, managing everything from basic functions like breathing and heart rate to complex tasks like thinking, learning, and decision-making. It is vital to protect the brain from injury or damage, as even small disruptions can affect our cognitive abilities, physical coordination, and overall well-being. Keeping the brain healthy helps maintain mental clarity, emotional balance, and quality of life.
Citations:
Medicine, UPMC. “Concussion Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments.” UPMC, https://www.upmc.com/services/orthopaedics/conditions/concussion#:~:text=Between%201.7%20and%203%20million,get%20a%20concussion%20this%20year.
“How Long Does a Concussion Last?” Cleveland Clinic, 24 Feb. 2024, https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15038-concussion
Staff, Mayo Clinic. “Concussion.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 12 Jan. 2024, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/concussion/symptoms-causes/syc-20355594
Oxford, University of. “Concussion.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 12 Jan. 2024, https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2023-01-31-three-or-more-concussions-linked-worse-brain-function-later-life#:~:text=athletes%20or%20employees.-,',processing%20speed%20and%20working%20memory.
CDC. “Preventing TBI.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 16 May 2024, https://www.cdc.gov/traumatic-brain-injury/prevention/index.html



Comments